BRANCHES OF PHYSICS:
A branch of physics, which is mainly concerned with the laws of motion and gravitation of Sir Isaac Newton and James Clark Maxwell’s Kinetic theory and thermodynamics, is called classical physics. Classical physics is mainly concerned with matter and energy. In classical physics energy and matter are considered as separate entities. Acoustics, Optics, Classical mechanics and electromagnetics are the traditional branches of classical physics. Moreover, any theory of physics, which is considered null and void in the modern physics, automatically falls under the realm of classical physics.
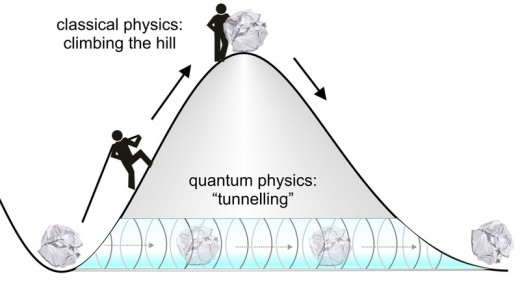
Classical Physics vs Quantum Physics | Source
Modern Physics
Modern physics is the branch of physics, which is mainly concerned with the theory of relativity and quantum mechanics. Albert Einstein and Max Plank were the pioneers of modern of physics. They were the first scientists who laid down the foundations of modern physics by introducing the theory of relativity and quantum mechanics respectively. In modern physics energy and matter are not considered as separate entities; rather they are considered as different forms of each other.
Nuclear Physics
Nuclear physics is the branch of physics which deals with constituents, structure, behaviour and interactions of atomic nuclei. Encarta dictionary defines the nuclear physics as “the branch of physics in which the structure, forces, and behavior of the atomic nucleus are studied.” In the modern age, nuclear physics has got a very wide scope. It is used in power generation, nuclear weapons, medicines etc.
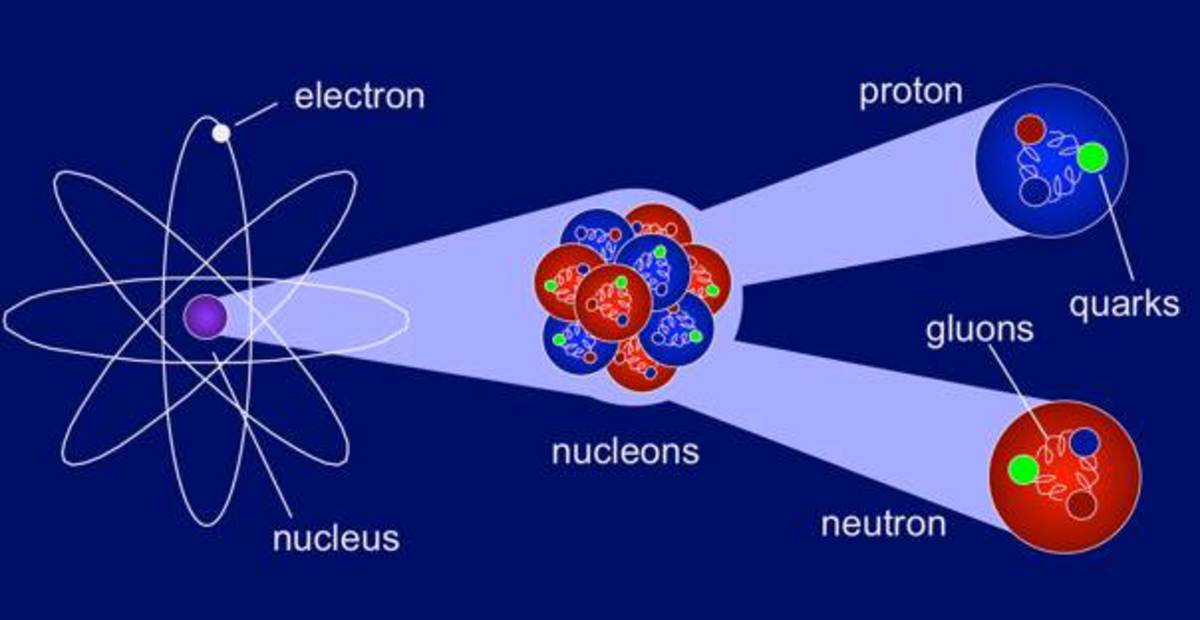
Nuclear Physics Definition | Source
No comments:
Post a Comment